Abstract
BACKGROUND: Coronary calcification negatively impacts optimal stenting. Intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) is a new calcium modification technique.
AIMS: We aimed to assess the impact of different calcium morphologies on IVL efficacy.
METHODS: This was a prospective, multicentre study (13 tertiary referral centres). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) was performed before and after IVL, and after stenting. OCT-defined calcium morphologies were concentric (mean calcium arc >180°) and eccentric (mean calcium arc ≤180°). The primary outcomes were angiographic success (residual stenosis <20%) and the presence of fracture by OCT in concentric versus eccentric lesions.
RESULTS: Ninety patients were included with a total of 95 lesions: 47 concentric and 48 eccentric. The median number of pulses was 60 (p=1.00). Following IVL, the presence of fracture was not statistically different between groups (79.0% vs 66.0% for concentric vs eccentric; p=0.165). The number of fractures/lesion (4.2±4.4 vs 2.3±2.8; p=0.018) and ≥3 fractures/lesion (57.1% vs 34.0%; p=0.029) were more common in concentric lesions. Angiographic success was numerically but not statistically higher in the concentric group (87.0% vs 76.6%; p=0.196). By OCT, no differences were noted in final minimum lumen area (5.9±2.2 mm2 vs 6.2±2.1 mm2; p=0.570), minimum stent area (5.9±2.2 mm² vs 6.25±2.4 mm2; p=0.483), minimum stent expansion (80.9±16.7% vs 78.2±19.8%), or stent expansion at the maximum calcium site (100.6±24.2% vs 95.8±27.3%) (p>0.05 for all comparisons of concentric vs eccentric, respectively). Calcified nodules were found in 29.5% of lesions; these were predominantly non-eruptive (57%). At the nodule site, dissection was more common than fracture with stent expansion of 103.6±27.2%.
CONCLUSIONS: In this prospective, multicentre study, the effectiveness of IVL followed by stenting was not significantly affected by coronary calcium morphology.
Coronary calcification continues to present a challenge in performing optimal percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Approximately 25% of patients presenting for PCI have a calcified lesion which is known to result in a higher incidence of major adverse cardiac events, particularly target lesion revascularisation (TLR) at midterm follow-up12. Many mechanisms have been put forward, including the difficulty in delivery of and mechanical damage to stents, as well as stent underexpansion. Stent underexpansion and, in particular, small minimum stent area (MSA) are known to be associated with stent failure34. The lack of compliance of calcified vessels is predominantly thought to account for poor expansion following stenting5. To address this problem, the use of plaque preparation techniques, whose aim is to improve vessel compliance prior to stenting, is recommended. One such technique is intravascular lithotripsy (IVL), a novel technique using a series of emitters encased within a balloon delivery system. Electrical pulses from the emitters are converted to acoustic energy waves within the balloon fluid and transmitted to the vessel wall6. When calcium is encountered, compression and decompression waves result in fracture, altering the rigidity of the atheromatous plaque and allowing expansion6. In this regard, the mechanism of action of IVL differs from those of high-pressure balloons or atherectomy techniques.
Initially, IVL was used predominantly in the context of severely calcified lesions defined by angiography. Data on the effectiveness of IVL in different calcified morphologies remain limited. Blachutzik et al used an angiographic definition of concentric and eccentric calcification and reported no differences in angiographic or clinical success7. However, angiography is known to be poorly sensitive for the detection of coronary calcium8. Conversely, intracoronary imaging with optical coherence tomography (OCT) has better sensitivity for calcium detection and provides unique insights on calcium location, distribution and pattern8. Recently, using an OCT definition, the effect of IVL on lesions containing nodules was reported9. However, reports on real-world experience of IVL and its effect on different calcium morphologies, as defined using intracoronary imaging, are limited. To address this void in knowledge, we performed a prospective, multicentre study with prespecified OCT assessment to determine the efficacy of IVL in different calcium morphologies.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
This was an investigator-initiated, prospective, multicentre, single-arm study involving 13 tertiary care centres in Spain and Italy. Consecutive patients undergoing IVL for the treatment of calcified coronary artery disease were included. Patients were excluded if they required atherectomy techniques (rotational, orbital or laser) prior to IVL treatment or if they had chronic kidney disease with an estimated glomerular filtration rate <15 ml/min/1.73 m2. All patients signed written informed consent, and the study was approved by the ethics committee at each participating centre. Follow-up for clinical events was also performed at the participating centres, and standard definitions for clinical events were used10. The study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04698902.
INTRAVASCULAR LITHOTRIPSY PROCEDURE
Centres were advised to select an IVL balloon based on vessel sizing by OCT. A 1:1 balloon-artery ratio was recommended. The number of pulses per cycle and total number of pulses delivered were at the discretion of the treating physician. Dilation after IVL was also at the discretion of the treating physician, while predilation was recommended only in the case of failure to advance an intracoronary imaging catheter.
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY PROCEDURE
OCT was mandatory and prespecified. It was performed using commercially available systems (Dragonfly OpStar [Abbott] and Lunawave [Terumo]) and was mandated prior to IVL treatment, immediately following IVL treatment and after final stenting and optimisation. Predilation with a small semicompliant balloon was permitted before IVL treatment to allow passage of the IVL or imaging catheter. All centres transferred both angiographic and OCT images to the coordinating centre for core lab analysis.
ANGIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS
Quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) of procedural angiograms was performed in a core lab (Hospital ClÃnico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain) using the Caas Workstation software (Pie Medical Imaging). Lesion parameters were assessed by QCA at baseline, after IVL and after stenting. The examined parameters included percentage diameter stenosis (%DS), lesion length, and calcium length. The acute gain by QCA was calculated as post-PCI minimum lumen diameter–pre-PCI minimum lumen diameter.
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGAPHY ANALYSIS
OCT analysis was also performed in a core lab (Hospital ClÃnico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain) using dedicated software (AptiVue Offline Review Software [Abbott] or QIVUS [Medis Medical Imaging Systems] for OCTs performed using Lunawave). Cross-sectional OCT analysis was performed at 1 mm intervals along the entire lesion length. Standard OCT definitions were used11. The Fujino calcium score, which predicts stent underexpansion, was also calculated12. Calcium was defined as a signal-poor region with well-demarcated borders. The mean reference (proximal+distal/2) diameters and areas were used in all analyses. The mean calcium arc along the length of the lesion treated with IVL was calculated by summing the calcium arc at each 1 mm interval and dividing by the total length of the lesion in mm. Concentric calcium was defined as a mean calcium arc along the length of the lesion of >180 degrees. Eccentric calcium was a mean calcium arc along the length of the lesion of ≤180 degrees. Nodular calcium was defined as a calcific protrusion into the lumen and was further classified as eruptive (nodular protrusion into the lumen with an irregular surface and no overlying fibrous cap) or non-eruptive (nodular protrusion into the lumen with a smooth surface and a fibrous cap). A subÂanalysis of lesions containing nodules was performed to assess fracture and expansion following IVL in nodular calcium. Following IVL and stenting, nodules were defined as being deformed (compression of the nodule following stenting without significant luminal protrusion) or non-deformed (no/minimal compression of the nodule following stenting with persistent protrusion into the lumen).
The area stenosis was calculated as (mean reference lumen area–minimum lumen area [MLA])/mean reference lumen area). Stent expansion was calculated as (MSA/mean reference lumen area)*100. The mean stent expansion and stent expansion at the maximum calcium site were calculated in the same way. The asymmetry index was calculated as 1–(minimum lumen diameter of the entire segment/maximum lumen diameter of the entire segment), with a value ≥0.3 considered asymmetric. The eccentricity index was calculated as the minimum lumen diameter/maximum lumen diameter from the same cross-section, with a value ≤0.7 considered eccentric13.
STUDY ENDPOINTS
The primary angiographic endpoint was angiographic success, defined as a residual stenosis following IVL and stenting of <20% in concentric versus eccentric calcification. The primary OCT endpoint was the number of fractures in concentric versus eccentric calcification. Secondary outcomes included the length and depth of fracture, stent expansion, stent malapposition, and MSA in concentric versus eccentric calcium.
STATISTICAL METHODS
Categorical variables were expressed as number and percentage (%), while continuous variables were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR) depending on the distribution. Normality was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 or Fisher’s exact test, and differences in continuous variables were compared using a 2-sided t-test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Freedom from all-cause mortality and TLR at 12 months were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. All data were analysed using STATA 15.1 (StataCorp).
Results
Ninety-six patients (102 lesions) were included from 13 centres. After assessment, 6 patients (7 lesions) were excluded because of poor OCT quality, resulting in a cohort of 90 patients with a total of 95 lesions (Supplementary Figure 1). By OCT, 47 lesions had predominantly concentric calcification, while 48 had predominantly eccentric calcification (Central illustration). Patient demographics are shown in Table 1. The mean age was 72.5±9.1 years with a male predominance (73.3%). Most patients had chronic coronary syndromes. The left anterior descending artery (LAD) was the most commonly treated vessel.
There were no differences in procedural aspects between concentric and eccentric lesions (Table 2). A high proportion of predilation was performed (62.2% vs 72.9%; p=0.270 for concentric vs eccentric, respectively). One IVL catheter per lesion was used in most cases, with the maximum IVL balloon diameter being 3 mm in both groups (p=1.00). The mean IVL balloon-artery ratio was ~1.2 by QCA and OCT across both groups (p>0.05). The median number of IVL pulses delivered was 60, without differences across the groups (p=1.00). Most lesions were stented using 1 stent and >90% were postdilated across both groups. One distal wire perforation occurred, which was managed conservatively. No perforations occurred during or after IVL therapy. Slow flow was seen in 2 patients, although neither case was related to the IVL therapy (1 before IVL therapy and 1 after stenting). Distal edge dissection that required further stenting occurred in 3 lesions. Transient side branch loss occurred in 1 patient after stenting using a provisional approach. There were no in-hospital deaths following IVL therapy.
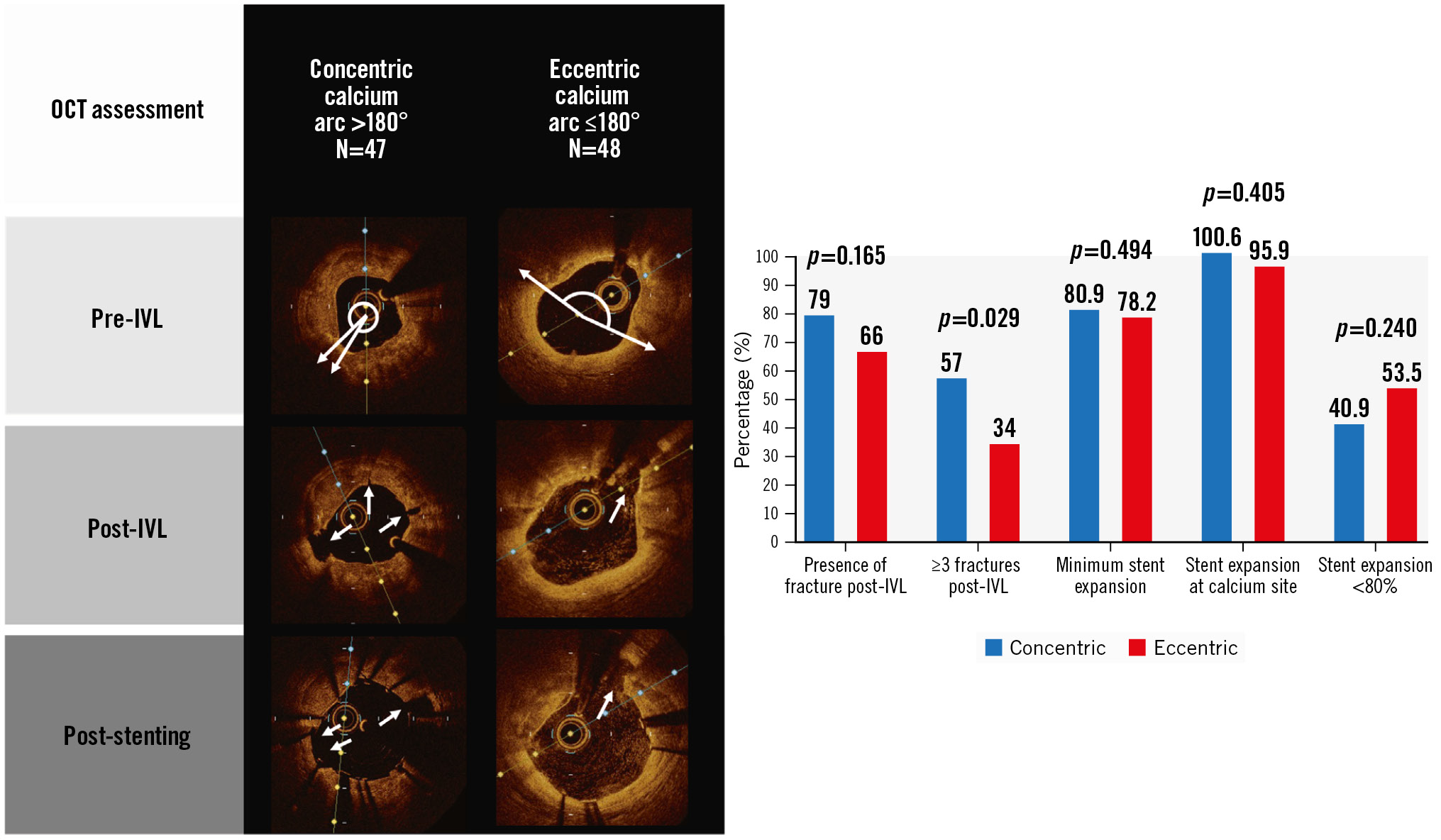
Central illustration. Overview of the important study findings. The OCT images (A) depict typical findings in concentric and eccentric lesions, with white arrows highlighting the fracture within the calcium. B) The chart depicts the main results after IVL and stenting in concentric and eccentric lesions. IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; OCT: optical coherence tomography
Table 1. Baseline demographics of patients undergoing IVL treatment.
| N=90 | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 72.5±9.1 |
| Female sex | 24 (26.7) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.1±4.1 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 41 (45.5) |
| Insulin use | 12 (29.3) |
| Hypertension | 69 (76.7) |
| Hyperlipidaemia | 71 (78.9) |
| Smoking | 36 (40.0) |
| Baseline eGFR, ml/min/1.73 m2 | 78.5±19.1 |
| eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 | 14 (15.7) |
| Coronary artery disease | 38 (42.2) |
| Previous MI | 22 (24.4) |
| Previous PCI | 26 (28.9) |
| Prior CABG | 7 (7.8) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 11 (12.2) |
| Previous permanent pacemaker | 4 (4.4) |
| COPD | 8 (8.9) |
| Previous cerebrovascular accident/TIA | 5 (5.6) |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 9 (10.0) |
| Baseline haemoglobin, g/dl | 13.0±1.6 |
| LVEF, % | 54.6±9.6 |
| Indication for PCI | |
| Stable angina/silent ischaemia | 56 (62.2) |
Acute coronary syndrome: unstable angina, STEMI, NSTEMI | 34 (37.8) |
| Procedural aspects | |
| Vascular access | |
| Radial artery | 74 (82.2) |
| Femoral artery | 16 (17.8) |
| Contrast volume, ml | 222.0±86.9 |
| Procedure time, min | 88 [63-170] |
| Acute kidney injury after procedure – all stage 1* | 5 (6.8) |
| Vascular access complications | 4 (5.1) |
| Length of hospital stay, days | 2 [1-4] |
| In-hospital deaths | 0 (0) |
| Medications on discharge | |
| Aspirin | 88 (97.8) |
| Second antiplatelet | 84 (93.3) |
| Anticoagulant | 11 (12.8) |
| Statin | 80 (89.9) |
| Data are presented as mean±SD, n (%) or median [IQR]. *Data available for 74 patients. CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; IQR: interquartile range; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MI: myocardial infarction; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SD: standard deviation; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; TIA: transient ischaemic attack | |
Table 2. Procedural aspects
| Procedural aspects per lesion | Overall populationN=95 | ConcentricN=47 | EccentricN=48 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary artery treated | 0.381 | |||
| Left main stem | 6 (6.3) | 1 (2.1) | 5 (10.4) | |
| Left anterior descending | 61 (64.2) | 31 (66.0) | 30 (62.5) | |
| Left circumflex | 10 (10.5) | 6 (12.8) | 4 (8.3) | |
| Right coronary | 18 (18.9) | 9 (19.2) | 9 (18.7) | |
| Plaque modification pre-IVL | ||||
| Balloon predilation | 63 (67.7) | 28 (62.2) | 35 (72.9) | 0.270 |
| Compliant balloon | 49 (77.8) | 23 (82) | 26 (76.5) | 0.787 |
| Non-compliant balloon | 16 (25.4) | 7 (25) | 9 (25.7) | 0.541 |
| Cutting/scoring balloon | 14 (22.6) | 7 (25) | 7 (20.6) | 0.506 |
| Maximum diameter of predilation balloon, mm | 2.5 [2.0-2.5] | 2.25 [2.0-2.5] | 2.5 [2.0-2.5] | <0.001 |
| IVL characteristics | ||||
| Number of IVL balloons used per vessel | ||||
| 1 IVL balloon | 83 (88.3) | 40 (87.0) | 43 (89.6) | 0.692 |
| ≥2 IVL balloons | 11 (11.7) | 6 (13.0) | 5 (10.4) | 0.511 |
| Maximum diameter of IVL balloon used, mm | 3.0 [2.5-3.5] | 3.0 [2.5-3.5] | 3.0 [3.0-3.5] | 1.00 |
| Balloon-artery ratio QCA | 1.20±0.22 | 1.18±0.18 | 1.18±0.25 | 0.989 |
| Balloon-artery ratio OCT | 1.23±0.24 | 1.26±0.25 | 1.23±0.23 | 0.576 |
| Number of pulses administered per vessel | 60 [40-80] | 60 [40-80] | 55 [40-80] | 1.00 |
| Plaque modification post-IVL | ||||
| Balloon post-dilation | 23 (24.5) | 13 (28.3) | 10 (20.8) | 0.402 |
| Balloon angioplasty (compliant) | 3 (11.1) | 2 (13.3) | 1 (8.3) | 0.681 |
| Balloon angioplasty (non-compliant) | 20 (86.9) | 13 (86.7) | 7 (58.3) | 0.095 |
| Cutting/scoring balloon | 6 (22.2) | 3 (20.0) | 3 (25.0) | 0.476 |
| Maximum diameter of balloon after IVL, mm | 3 [3.0-3.5] | 3.25 [3.0-3.5] | 3 [3.0-3.5] | 1.00 |
| PCI characteristics | ||||
| Number of stents per vessel | 1 [1-1] | 1 [1-1] | 1 [1-1] | 1.00 |
| Total stented length, mm | 26 [18-38] | 26 [18-40] | 26 [21-33.5] | 1.00 |
| Mean stent diameter, mm | 3.0 [2.75-3.5] | 3.0 [2.75-3.5] | 3.0 [2.75-3.5] | 1.00 |
| Post-dilation | 86 (92.5) | 43 (93.5) | 43 (91.5) | 0.716 |
| Maximum diameter of post-dilation balloon, mm | 3.5 [3.0-3.5] | 3.5 [3.0-3.5] | 3.5 [3.0-3.5] | 1.00 |
| Data are presented as n (%), median [IQR] or mean±SD. IQR: interquartile range; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; SD: standard deviation | ||||
LESION ASSESSMENT BY QUANTITATIVE CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
Table 3 and Figure 1 show QCA parameters before IVL, after IVL and after stenting. A sequential decrease was seen in the %DS from baseline to after IVL and after stenting for both calcium morphologies. No difference in final %DS was found between groups (12.2±11.1% vs 12.5±10.0% for concentric vs eccentric calcium, respectively; p=0.894). Acute luminal gain was not different between groups (1.27±0.45 mm vs 1.25±0.51 mm; p=0.820). The primary outcome of angiographic success by QCA was numerically higher in the concentric group, but this was not statistically significant (87.0% vs 76.6%; p=0.196). Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) III flow was achieved in 98% of lesions without between-group differences.
Table 3. Quantitative coronary angiography assessment of lesions pre-IVL, post-IVL, and post-stenting.
| Procedural aspects – QCA data | Overall populationN=95 | ConcentricN=47 | EccentricN=48 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angiographic characteristics | ||||
| Pre-IVL | ||||
| Lesion length by QCA, mm | 20.4±9.7 | 21.5±10.9 | 19.3±8.4 | 0.270 |
| Percentage stenosis by QCA, % | 58.2±2.3 | 58.3±11.8 | 58.1±12.8 | 0.943 |
| Minimum diameter by QCA, mm | 1.14±0.38 | 1.14±0.33 | 1.15±0.43 | 0.921 |
| Reference diameter, mm | 2.7±0.58 | 2.72±0.61 | 2.69±0.56 | 0.797 |
| Type B2/C lesion | 89 (93.7) | 44 (93.6) | 45 (93.7) | 1.00 |
| Post-IVL | ||||
| Percentage stenosis by QCA, % | 34.9±15.8 | 36.2±16.2 | 33.6±15.4 | 0.446 |
| Minimum diameter by QCA, mm | 1.63±0.43 | 1.61±0.42 | 1.66±0.44 | 0.592 |
| Acute diameter gain, mm | 0.31±0.67 | 0.29±0.62 | 0.34±0.72 | 0.712 |
| Post-stenting and optimisation (in stent)* | ||||
| Percentage stenosis by QCA, % | 12.4±10.5 | 12.24±11.1 | 12.53±10 | 0.894 |
| Minimum diameter by QCA, mm | 2.41±0.44 | 2.41±0.45 | 2.41±0.43 | 0.894 |
| Acute luminal gain by QCA, mm | 1.26±0.48 | 1.27±0.46 | 1.26±0.47 | 0.904 |
| Final percentage stenosis <50% | 92 (98.9) | 45 (97.8) | 47 (100) | 0.545 |
| Final percentage stenosis <30% | 89 (95.7) | 44 (95.7) | 45 (95.7) | 0.982 |
| Final percentage stenosis <20% | 76 (82.0) | 40 (87.0) | 36 (76.6) | 0.196 |
| TIMI III flow | 90 (97.83) | 42 (95.5) | 48 (100) | 0.135 |
| Post-stenting and optimisation (in segment) | ||||
| Percentage stenosis by QCA, % | 15.7±12.6 | 17.68±12.9 | 13.9±12.2 | 0.156 |
| Minimum diameter by QCA, mm | 2.05±0.48 | 2.01±0.45 | 2.08±0.50 | 0.503 |
| Acute luminal gain by QCA, mm | 0.9±0.52 | 0.88±0.51 | 0.91±0.54 | 0.767 |
| Data are presented as mean±SD or n (%). *Data are available for 93 lesions. IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; SD: standard deviation; TIMI: Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction | ||||
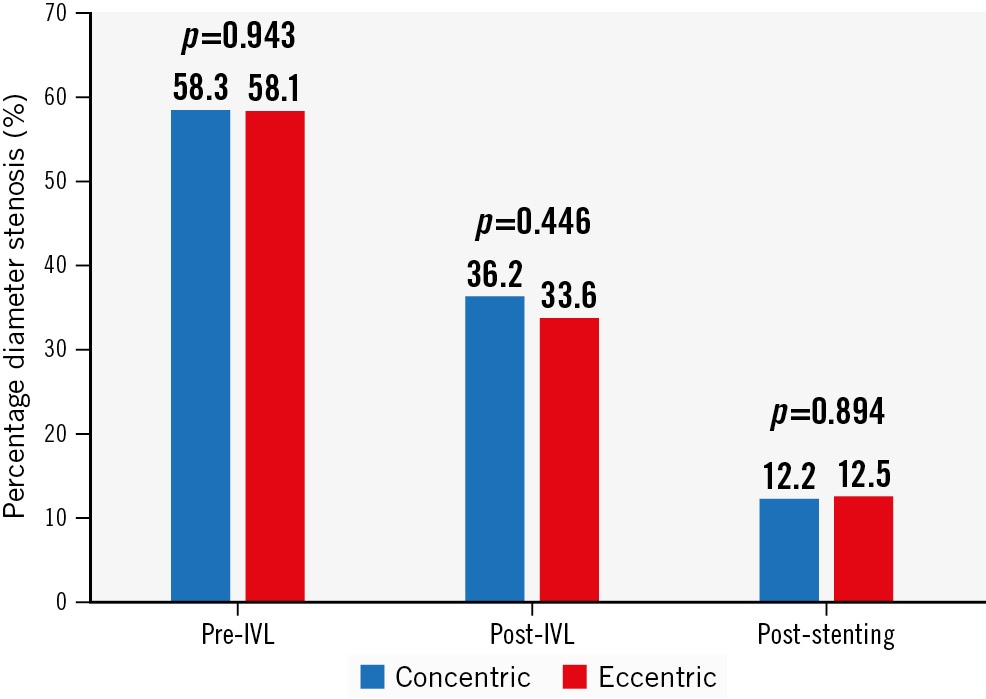
Figure 1. Changes in percentage diameter stenosis by quantitative coronary angiography from baseline to after IVL, and after stenting (in stent). IVL: intravascular lithotripsy
LESION ASSESSMENT BY OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
OCT demonstrated a significant calcium burden across both groups (Table 4). As expected, based on the definitions used, concentric lesions had a larger mean calcium arc (229.9±47.2 degrees vs 145.8±27.9 degrees), maximum calcium arc (339.9±31.2 degrees vs 269.1±67.6 degrees) and calcium volume index (4,424±2,492 vs 2,739±1,720) than eccentric lesions (p<0.05 for all comparisons). Baseline percentage area stenosis (69.9±12.7% vs 64.8±14.6%; p=0.079) and MLA (1.78±0.74 mm2 vs 1.99±0.68 mm2; p=0.151) were not different across groups, but concentric lesions tended towards greater percentage stenosis and a smaller MLA. The OCT calcium score (as defined by Fujino et al12) was 4 in most patients.
Following IVL, visible calcium fracture by OCT was numerically more common in concentric lesions, but without statistical significance (79% vs 66%; p=0.165). All other fracture parameters were greater in concentric than in eccentric lesions, including the total number of fractures per lesion (4.2±4.4 vs 2.3±2.8; p=0.018), the presence of 3 fractures per lesion (57.1% vs 34.0%; p=0.029), fracture width (0.62±0.29 mm vs 0.42±0.27 mm; p=0.005), fracture depth (0.92±0.35 mm vs 0.68±0.35 mm; p=0.008) and fracture arc (37.2±23.9 degrees vs 24.5±14.6 degrees; p=0.014) (Central illustration, Figure 2). Dissection was common and occurred in three-quarters of lesions after IVL. Typical OCT findings in concentric and eccentric calcium are presented in the Central illustration.
A sequential increase in MLA across both groups following IVL and stenting was seen without differences in final in-stent MLA (5.9±2.2 mm2 vs 6.2±2.1 mm2 for concentric vs eccentric, respectively; p=0.570) (Figure 3). Similarly, there were no differences in MSA between groups (5.9±2.2 mm² vs 6.25±2.4 mm2 for concentric vs eccentric, respectively; p=0.483) (Figure 2). Stent parameters such as minimum stent expansion (80.9±16.7% vs 78.2±19.8%) and expansion at maximum calcium site (100.6±24.2% vs 95.9±27.3%) were not different between groups (p>0.05 for all comparisons) (Central illustration). Stent symmetry and eccentricity indices improved following stenting and were not different between groups. Significant malapposition (>0.4 mm) was more common in eccentric lesions.
Table 4. Optical coherence tomography lesion assessment pre-IVL, post-IVL, and post-stenting.
| Procedural aspects – OCT data | Overall populationN=95 | ConcentricN=47 | EccentricN=48 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-IVL | ||||
| Lesion length, mm | 23.7±10.7 | 24.0±11.7 | 23.5±9.6 | 0.852 |
| Mean reference lumen area*, mm2 | 6.4±2.6 | 6.58±3.0 | 6.23±2.1 | 0.531 |
| Mean reference lumen diameter$, mm | 2.79±0.58 | 2.81±0.66 | 2.77±0.50 | 0.740 |
| Distal reference diameter, mm | 2.56±0.67 | 2.58±0.80 | 2.52±0.55 | 0.741 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 1.88±0.71 | 1.78±0.74 | 1.99±0.68 | 0.151 |
| Mean diameter at MLA, mm | 1.51±0.30 | 1.46±0.29 | 1.55±0.31 | 0.154 |
| Minimum diameter at MLA, mm | 1.22±0.29 | 1.23±0.28 | 1.20±0.30 | 0.746 |
| Percentage area stenosis, % | 67.4±1.65 | 69.9±12.7 | 64.8±14.6 | 0.079 |
| Percentage diameter stenosis, % | 57.5±11.65 | 57.3±11.9 | 57.7±11.5 | 0.860 |
| Asymmetry index** | 0.69±0.1 | 0.69±0.1 | 0.69±0.1 | 0.775 |
| Asymmetry index >0.3** | 90 (100) | 46 (100) | 44 (100) | 1.00 |
| Eccentricity index** | 0.49±0.1 | 0.52±0.1 | 0.47±0.1 | 0.034 |
| Eccentricity index <0.7** | 89 (98.8) | 46 (100) | 43 (97.7) | 1.00 |
| Extent of calcification | ||||
| Maximum calcium arc, degrees | 304.5±62.2 | 339.9±31.2 | 269.1±67.6 | <0.001 |
| Lumen area at maximum calcium site, mm2 | 3.13±1.58 | 2.77±1.49 | 3.50±1.61 | 0.030 |
| Calcium thickness at maximum calcium site, mm | 0.88±0.29 | 0.83±0.27 | 0.95±0.30 | 0.096 |
| Mean calcium arc, degrees | 188.3±57.3 | 229.9±47.2 | 145.79±27.9 | <0.001 |
| Calcium arc at MLA, degrees | 259.6±95.3 | 303.8±76.6 | 215.4±92.3 | <0.001 |
| Calcium thickness at MLA, mm | 0.85±0.33 | 0.87±0.32 | 0.82±0.36 | 0.604 |
| Maximum calcium thickness, mm | 1.13±0.25 | 1.1±0.26 | 1.18±0.24 | 0.075 |
| Calcium length, mm | 18.9±9.5 | 18.9±9.1 | 18.9±9.9 | 0.989 |
| Calcium volume index | 3,610±2,303 | 4,424±2,492 | 2,739±1,720 | <0.001 |
| Fujino OCT calcium score=412# | 86 (90.5) | 45 (95.7) | 41 (85.4) | 0.091 |
| Post-IVL | ||||
| Percentage area stenosis, % | 43.5±15.1 | 43.5±16.3 | 43.5±14.0 | 1.00 |
| Percentage diameter stenosis, % | 40.2±13.4 | 38.9±12.6 | 41.4±14.1 | 0.384 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 3.6±1.14 | 3.6±1.2 | 3.6±1.1 | 0.860 |
| Minimum diameter at MLA, mm | 1.70±0.38 | 1.70±0.34 | 1.64±0.41 | 0.362 |
| Mean diameter at MLA, mm | 2.1±0.34 | 2.1±0.34 | 2.1±0.35 | 0.799 |
| Post-IVL: calcium fracture characteristics | n=89 | n=89 | n=89 | n=89 |
| Presence of calcium fractures | 65 (72.2) | 34 (79) | 31 (65.96) | 0.165 |
| ≥3 visible fractures | 40 (45) | 24 (57.1) | 16 (34.0) | 0.029 |
| Total number of fractures per lesion | 3.18±3.7 | 4.2±4.4 | 2.3±2.8 | 0.018 |
| Fracture width, mm | 0.52±0.30 | 0.62±0.29 | 0.42±0.27 | 0.005 |
| Fracture depth, mm | 0.80±0.37 | 0.92±0.35 | 0.68±0.35 | 0.008 |
| Length of fracture, mm | 3.42±2.60 | 3.7±3.16 | 3.10±1.85 | 0.360 |
| Fracture arc, degrees | 31.25±20.95 | 37.2±23.9 | 24.5±14.6 | 0.014 |
| Max no. of fractures per quadrant | 1.12±0.63 | 1.29±0.62 | 0.97±0.61 | 0.035 |
| No. of quadrants with fracture | 2.1±1.3 | 2.6±1.1 | 1.7±1.2 | 0.002 |
| Presence of dissections | 64 (74.4) | 31 (73.8) | 33 (75.0) | 0.899 |
| Dissection depth, mm | 0.42±0.17 | 0.44±0.18 | 0.40±0.15 | 0.444 |
| Dissection arc, degrees | 73.9±38.3 | 76.0±36.7 | 72.26±40.1 | 0.634 |
| Dissection length, mm | 2.85±2.18 | 2.56±1.37 | 3.10±2.65 | 0.577 |
| Minimum calcium arc where fracture is seen, degrees | 223.4±99.7 | 248.44±95.95 | 194.00±98.55 | 0.098 |
| No. of fractures at max calcium site | 1.02±1.1 | 1.14±1.1 | 0.90±1.1 | 0.308 |
| Max no. of fractures per single frame | 1.28±1.20 | 1.50±1.20 | 1.10±1.20 | 0.112 |
| Calcium arc at max no. of fractures, degrees | 271.4±106.4 | 293.5±97.6 | 248.4±112.1 | 0.132 |
| Post-stenting (in stent) | ||||
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 6.06±2.12 | 5.90±2.20 | 6.20±2.10 | 0.570 |
| Minimum stent area, mm2 | 6.08±2.26 | 5.90±2.18 | 6.25±2.40 | 0.483 |
| Mean stent area, mm2 | 7.94±2.55 | 7.70±2.60 | 8.14±2.50 | 0.455 |
| Stent area at MLA, mm2 | 6.98±2.10 | 6.97±2.10 | 7.00±2.14 | 0.939 |
| Mean reference area, mm2 | 7.93±3.19 | 7.62±3.24 | 8.23±3.15 | 0.373 |
| Minimum stent expansion, % | 79.6±18.25 | 80.9±16.67 | 78.2±19.77 | 0.494 |
| Stent expansion <80% | 47 (49.5) | 18 (40.9) | 24 (53.5) | 0.240 |
| Mean stent expansion, % | 105.28±19.6 | 107.7±18.1 | 102.9±20.9 | 0.265 |
| Stent area at max calcium site, mm2 | 7.31±2.12 | 7.10±2.15 | 7.53±2.10 | 0.372 |
| Stent expansion at maximum calcium site, % | 98.3±25.6 | 100.6±24.2 | 95.9±27.3 | 0.405 |
| Stent symmetry index | 0.41±0.10 | 0.40±0.10 | 0.42±0.10 | 0.434 |
| Stent symmetry index >0.3 | 80 (88.9) | 40 (86.9) | 40 (90.9) | 0.551 |
| Eccentricity index | 0.67±0.09 | 0.68±0.10 | 0.67±0.08 | 0.644 |
| Eccentricity index <0.7 | 53 (60.9) | 27 (61.4) | 26 (60.5) | 0.932 |
| Post-stenting (in segment) | ||||
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 4.87±2.26 | 4.92±2.50 | 4.81±2.00 | 0.821 |
| Malapposition | ||||
| Presence of malapposed struts | 58 (65.2) | 30 (68.2) | 28 (62.2) | 0.555 |
| Maximum malapposition distance, mm | 0.5±0.4 | 0.35±0.19 | 0.67±0.48 | 0.001 |
| Malapposition >0.4 mm | 26 (45.6) | 9 (30.0) | 17 (62.96) | 0.013 |
| Dissections | ||||
| Proximal edge dissection | 9 (10.5) | 4 (9.1) | 5 (11.9) | 0.670 |
| Distal edge dissection | 11 (12.8) | 6 (13.64) | 5 (11.9) | 0.810 |
| Data are presented as mean±SD or n (%). *Mean reference lumen area=(proximal reference lumen area+distal reference lumen area)/2. **Data are available for 90 lesions. $Mean reference lumen diameter=(proximal reference lumen diameter+distal reference lumen diameter)/2. #OCT calcium score based on the publication by Fujino et al12. IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; MLA: minimum lumen area; No.: number; OCT: optical coherence tomography | ||||
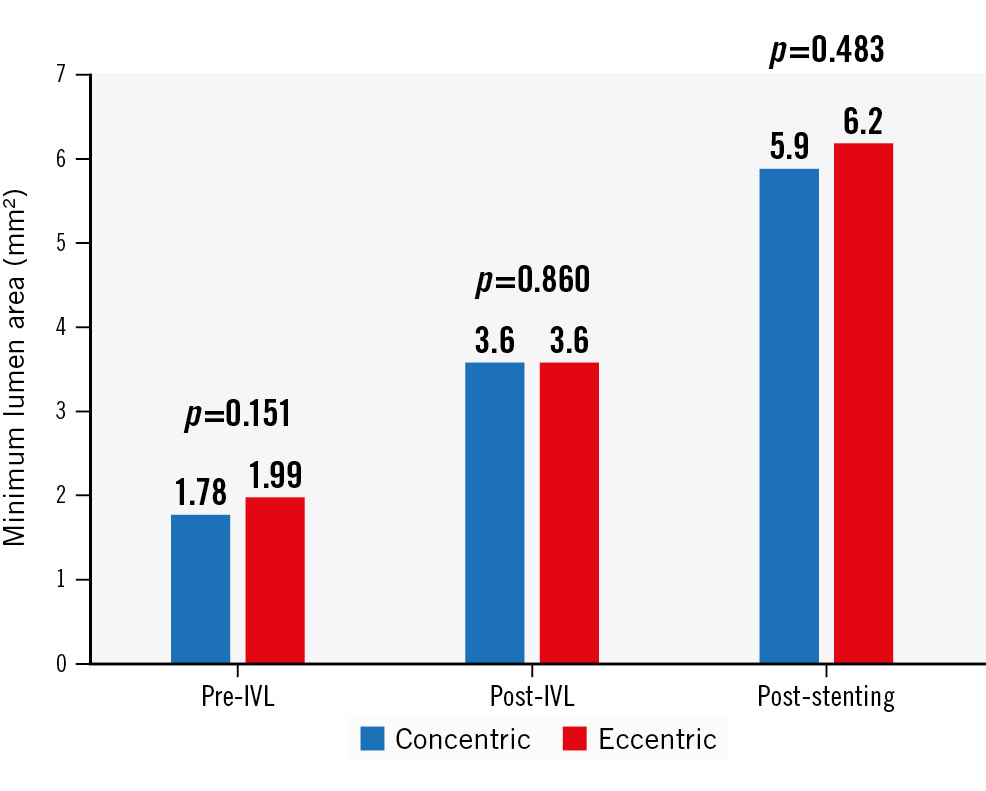
Figure 2. Changes in minimum lumen area by optical coherence tomography (OCT) from baseline to after IVL, and after stenting. IVL: intravascular lithotripsy
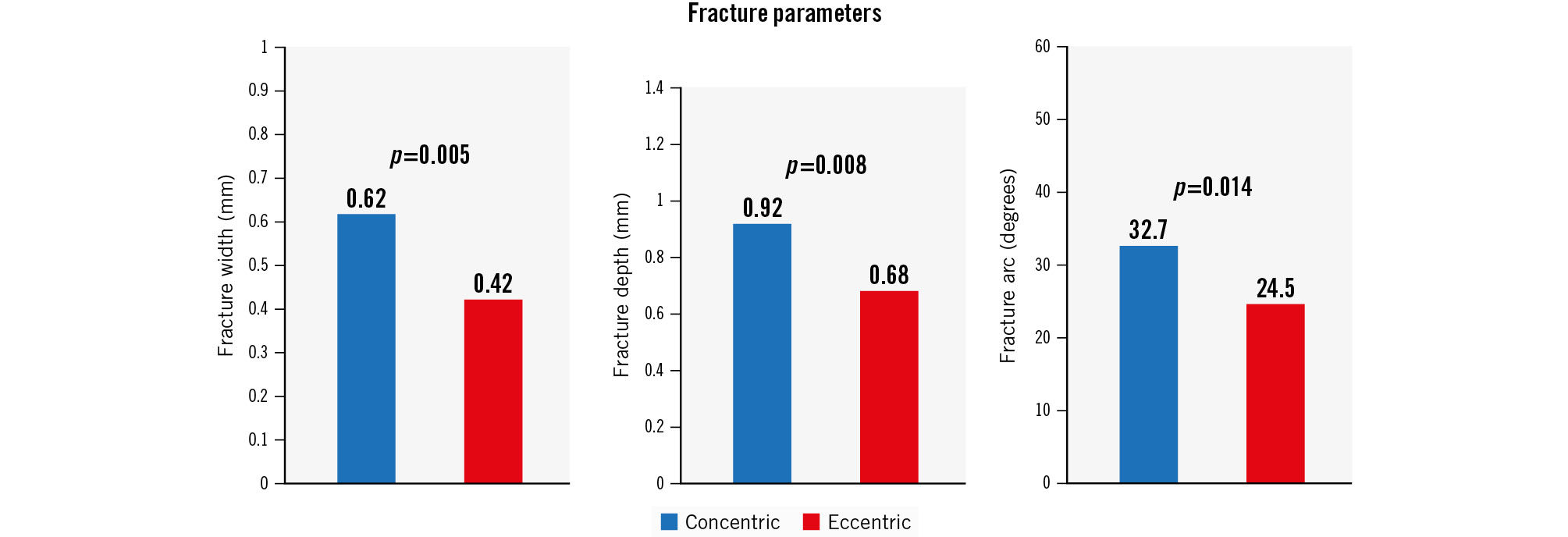
Figure 3. Fracture parameters in concentric and eccentric lesions including fracture width, fracture depth and fracture arc.
NODULAR CALCIFICATION
Calcified nodules were present in 28 lesions (29.5%) (Table 5). Almost half the nodules were within lesions in the LAD; however, as a proportion, nodules were more frequent in the right coronary (9 of 18) and left circumflex (4 of 10) arteries. The presence of a calcified nodule within a lesion was associated with an overall high burden of calcium, with the maximum calcium arc being 282 degrees and calcium thickness being 1.27 mm.
Nodule morphology was predominantly non-eruptive (57%) with the mean nodule arc spanning two quadrants (109.2±34 degrees). In 5 lesions, the nodule was at the MLA site. A progressive reduction in %DS with a corresponding increase in area at the nodule site was seen by OCT following IVL and stenting. At the site of the calcified nodule, dissection was common, while calcium fracture was less frequently seen. However, within lesions containing nodules, fracture in other calcified areas with nodules was common and seen in >70%. Stent expansion at the nodule site was 103.6±27.2%. Following stenting, only 40.7% of nodules were fully deformed and no longer protruding into the lumen. Malapposition at the nodule site was frequent, and malÂapposition>0.4 mm within the lesion containing a nodule was found in >70%. Figure 4 depicts eruptive and non-eruptive nodules by OCT as well as the appearance of deformed and non-deformed nodules after stenting.
Table 5. Optical coherence tomography assessment of lesions containing a calcified nodule pre-IVL, post-IVL, and post-stenting.
| OCT parameters | N=28 |
|---|---|
| Vessel with nodule | |
| Left main | 2 (7.14) |
| LAD | 13 (46.4) |
| LCx | 4 (14.3) |
| RCA | 9 (32.1) |
| Baseline OCT assessment pre-IVL | |
| Baseline calcified nodule lesion assessment | |
| Maximum calcium arc in CN lesion, degrees | 282.16±69.74 |
| Mean calcium arc in CN lesion, degrees | 170.36±57.00 |
| Maximum calcium thickness, mm | 1.27±0.24 |
| Calcium volume index | 3,477±2,279 |
| Baseline nodule assessment | |
| Nodule morphology | |
| Eruptive nodule | 11 (39.3) |
| Non-eruptive nodule | 16 (57.0) |
| Nodule arc, degrees | 109.2±34 |
| Nodule protrusion into the lumen, mm | 0.86±0.43 |
| Nodule length, mm | 4.6±2.8 |
| Lumen area at nodule, mm2 | 3.2±1.5 |
| Percentage area stenosis at nodule, % | 44.7±35.4 |
| Assessment post-IVL | |
| Area at nodule site, mm2 | 4.89±1.60 |
| Dissection at nodule site | 15 (57.69) |
| Fracture at nodule site | 4 (15.38) |
| Fracture within lesion containing a nodule | 19 (70.4) |
| Percentage area stenosis at nodule, % | 23.94±26.17 |
| Assessment post-stenting | |
| Deformation | 11 (40.7) |
| Area at nodule site, mm2 | 7.7±1.65 |
| Percentage expansion at nodule site, % | 103.6±27.2 |
| Expansion <80% at nodule site | 6 (23) |
| Malapposition at nodule site | 14 (58.3) |
| Malapposition along length of lesion containing a nodule | 21 (77.8) |
| Maximum malapposition distance, mm | 0.548±0.41 |
| Malapposition >0.4 mm | 20 (71.4) |
| Data are presented as n (%) or mean±SD. CN: calcified nodule; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCx: left circumflex artery; OCT: optical coherence tomography; RCA: right coronary artery; SD: standard deviation | |
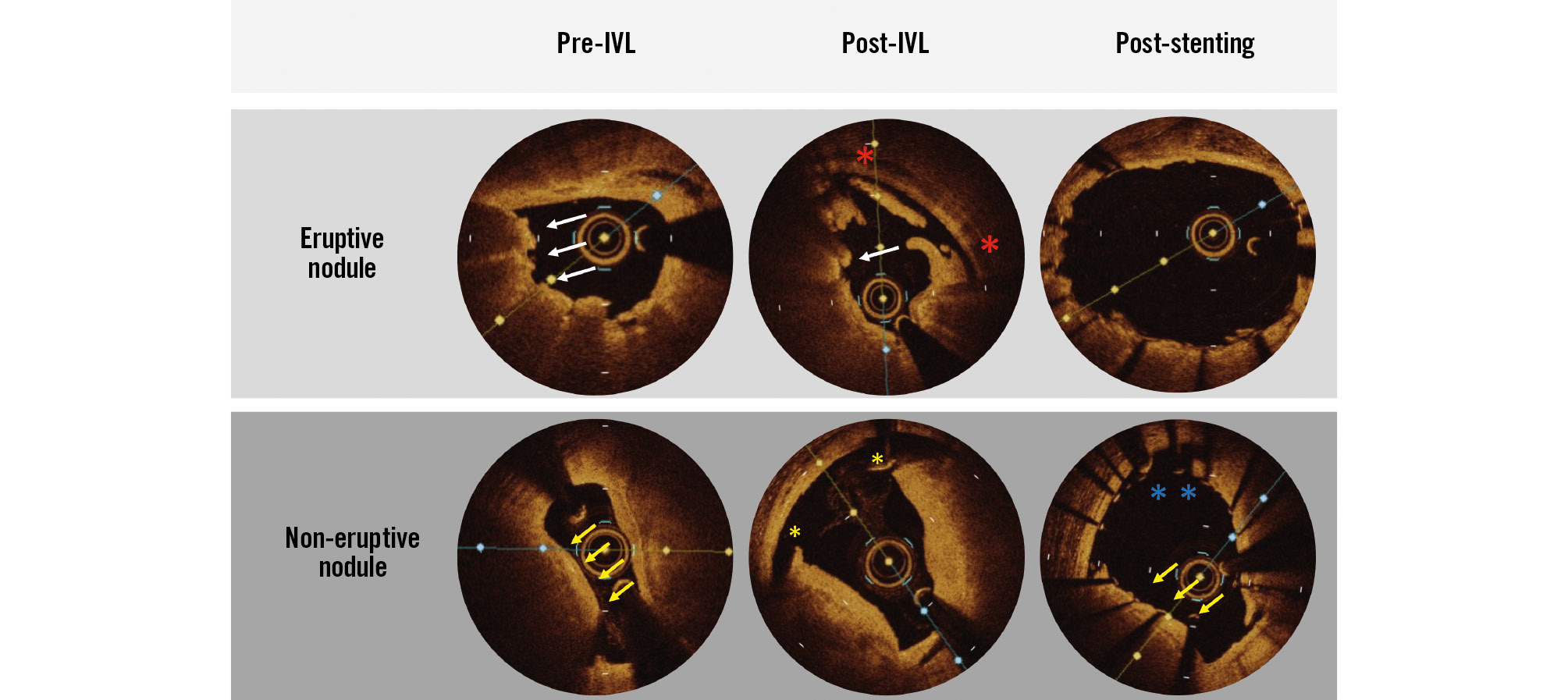
Figure 4. Typical optical coherence tomography findings of an eruptive and non-eruptive nodule. Note the irregular protrusion of the eruptive nodule into the lumen with a thin fibrous cap (white arrows). Conversely, the non-eruptive nodule demonstrates a thick fibrous cap (yellow arrows). After IVL, significant disruption can be seen at the nodule site in both the eruptive and non-eruptive nodules with dissection (red and yellow asterisks); however, fracture is not seen. After stenting, the eruptive nodule is deformed and no longer protrudes into the lumen, while the non-eruptive nodule is not deformed and continues to protrude (yellow arrows). The presence of malapposition can also be seen in the non-deformed nodule (blue asterisks). IVL: intravascular lithotripsy
CLINICAL FOLLOW-UP
The median follow-up was 362 days (IQR 238-498). No in-hospital deaths occurred. Freedom from all-cause mortality at 12 months was 96% (Supplementary Figure 2). Three patients died during this time: 2 of non-cardiovascular causes and 1 of sudden cardiac death. Freedom from TLR was 96% (Supplementary Figure 3). Four lesions required revascularisation, with the median time to TLR being 225 days (IQR 33-283). Two of these lesions presented as acute coronary syndromes with one being a definite stent thrombosis at 6 days after IVL.
Discussion
This prospective, multicentre study evaluated the effect of IVL on different calcium patterns. The main findings are as follows: 1) concentric and eccentric calcification were equally common in the present population; 2) while IVL results in calcium fracture in both concentric and eccentric calcification, IVL in concentric lesions results in a greater number of fractures, with wider, and deeper fractures; 3) despite greater fracture parameters in concentric calcium, there were no differences in final %DS by QCA between calcium morphologies; 4) OCT analysis confirmed that there were no differences in main stenting parameters including MSA, stent expansion and expansion at maximum calcium site, between concentric and eccentric calcium; 5) calcified nodules were found in 29.5% of lesions, and following IVL, dissection was more frequent than fracture at the nodule site; however, the mean stent expansion at the nodule site was >100%.
Calcified coronary artery disease is a frequent finding in the catheterisation lab and is not only a marker of lesion complexity but is also a marker of poor outcomes, both immediately and at longer term follow-up1. While a number of tools are available to treat coronary calcification, severe calcification often requires atherectomy techniques which have reported periprocedural complication rates of 2-4%14151617. Similar periprocedural complications have been reported with the use of modified and super-high pressure balloons1819. IVL offers a different mechanism of action in terms of calcium modification and utilises acoustic waves generated from emitters encased within a balloon delivery system6. The safety and efficacy of IVL has been shown in the Disrupt CAD series of studies, and a pooled analysis of these studies has shown low complication rates (perforation rate 0.2%)20. Small retrospective studies have also demonstrated IVL to be safe21.
Studies outside the Disrupt CAD series are, however, limited. Additionally, initial reports for the use of IVL shed doubt on its ability to fracture eccentric calcium. Our study represents a large, real-world cohort of patients with prespecified OCT assessment in both eccentric and concentric calcification and reports on both the safety and efficacy of this technique. Our population reflects those reported in other calcium modification studies, incorporating a predominantly male cohort with multiple cardiovascular risk factors151920. Additionally, in keeping with other studies, rates of pre- and post-dilation were high15. Reassuringly, despite the mandatory use of three runs of OCT, contrast volumes were in line with previous studies1522.
Angiographic assessment showed no significant differences between concentric and eccentric lesions. A sequential decrease in %DS with a corresponding increase in MLA was found in both groups, without differences in the final %DS. Furthermore, a residual %DS <30% was seen in >95% of patients, which is consistent with previous IVL studies20.
Similar to previous studies, the presence of calcium fracture was common across both groups, with concentric lesions having higher numbers of fractures, as well as deeper and wider fractures. A larger calcium arc has previously been associated with increased fracture following IVL, a finding that is reflected in our study given the greater number of fractures seen in concentric lesions23. Calcium fracture is widely considered to be necessary to alter vessel compliance and allow stent expansion, and this has been noted in other studies examining calcium modification techniques2425. Stent expansion tended to be higher in the concentric group, with a greater proportion of lesions having a minimum stent expansion >80%, which may have been related to the greater number of fractures in this group. However, overall, a high proportion of patients had stent expansion <80% (~50% of the entire cohort). Achieving optimum stent expansion in calcified lesions is difficult and excessive dilation may run the risk of perforation. In the PREPARE-CALC OCT substudy, which compared rotational atherectomy to modified balloons for calcified lesions, the minimum stent expansion across both groups was 73%, with >60% having expansion <80%25. Similar expansion was noted in the ISAR-CALC study, which compared super-high pressure balloons to modified balloons in calcified lesions (72% vs 68% for super-high pressure and modified balloons, respectively)18. Regarding IVL, OCT substudies of Disrupt CAD II and III found a minimum expansion of 77.6±20.5% and 78.4±25.8%, respectively2627, which overall aligns with our study, and is marginally better in comparison to the aforementioned studies using other techniques. Whether this small incremental increase in stent expansion with IVL translates to better longer-term outcomes versus other therapies remains to be elucidated.
Nodular calcium represents a morphology that is difficult to treat and is associated with stent recoil and device failure2829. In our study, ~30% of lesions included a calcified nodule with a high proportion in the right coronary and left circumflex arteries, consistent with previous intracoronary imaging and post-mortem studies93031. Following IVL therapy, fracture within a lesion containing a calcified nodule was common (70%); however, fracture within a nodule itself was uncommon (15.4%). Ali et al have also previously examined the effect of IVL on calcified nodules9. In their study, the rate of fracture within a nodule itself was not reported; however, the rate of fracture within a lesion containing a nodule was 78.9%, in line with our study9. This finding is unsurprising given that the lesions containing nodules were severely calcified, with a mean calcium arc of 170 degrees. However, despite less fracture, a sequential increase in MLA and a large subsequent MSA at the nodule site were noted, with stent expansion at this site being >100%. This was despite most nodules remaining non-deformed with residual luminal protrusion following stenting. This finding suggests that there is perhaps a different mechanism explaining the stent expansion seen at the nodule site. Greater dissection at this site, as seen by OCT in our study, may be a possible explanation. Additionally, the presence of microfracture, which is beyond the resolution of OCT, may be another explanation, but likely requires histological studies to further examine this hypothesis. Regardless of the mechanism, and despite stent expansion of >100%, significant malapposition was common at the nodule site. Further studies are required to determine if the use of combination calcium modification therapies could lead to greater nodule deformation with reduced malapposition following stenting.
The safety of IVL is once again confirmed in our study. Intraprocedural complications were low overall, with perforation and slow flow/no reflow being uncommon. Despite dissection being seen on OCT in up to 75% of patients, flow-limiting dissection was rare. Intraprocedural complications, particularly perforation, have heretofore been a considerable drawback when using advanced calcium modification techniques. In studies using rotational atherectomy, perforation rates have been in the region of 2-4%1415, while modified balloons and super-high pressure balloons have demonstrated similar rates1819. The improved safety profile with IVL is likely related to both the mechanism of action, which does not generate particulate matter that causes distal embolisation and slow/no flow, and the familiarity/ease of use for most interventional cardiologists of this balloon-based technology which uses low inflation pressures. Other registries and comparisons of IVL to other calcium modification technologies are ongoing (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04253171, NCT04428177, NCT04181268, NCT04298307).
The midterm outcomes in our cohort were akin to those seen in the 1-year follow-up of the Disrupt CAD III study32. Overall TLR and cardiac death rates were low and lower than those seen in previous studies of patients with severely calcified lesions undergoing PCI. A pooled analysis of the HORIZONS-AMI and ACUITY trials demonstrated a cardiac death rate of 4.0% and TLR rate of 8.7% at 1 year in patients with severely calcified lesions1. While the lower events rates in our study may be partially attributed to our smaller sample size, the mandatory use of intracoronary imaging before IVL, after IVL, and after stenting, which has been shown to reduce TLR rates, may have played a significant role24333435.
Limitations
A number of limitations must be acknowledged. Firstly, this is a single-arm trial without any comparison between IVL and other calcium modification tools. Secondly, predilation was allowed in the protocol if an OCT catheter could not be advanced, and, while atherectomy techniques were not permitted, cutting/scoring balloons were allowed; these were subsequently used in ~22% of lesions before IVL and ~22% after IVL. This may have led to dissections and calcium fracture that were attributed to IVL treatment. Thirdly, a number of lesions were excluded from analysis due to poor OCT pullback quality, although this number was small (7 lesions). Newer software, such as Ultreon (Abbott), that incorporates the use of artificial intelligence to detect calcium may reduce the number of OCT pullbacks deemed unsuitable for analysis. A number of parameters had numerically but not statistically significant differences, and this lack of statistical significance may have been due to the small sample size.
Conclusions
In this prospective, multicentre study, IVL was both safe and effective in different calcium morphologies, with no differences found in MSA or stent expansion between concentric and eccentric calcium despite a greater number of visible fractures in concentric calcification.
Impact on daily practice
Coronary calcium is frequently encountered during percutaneous coronary intervention and negatively affects both the acute and long-term results of stenting. Calcium modification is recommended before stenting, but much debate exists regarding the most appropriate technique for concentric and eccentric calcium. In this prospective study, calcium morphology (concentric vs eccentric) did not significantly impact the effectiveness of intravascular lithotripsy, with no difference in final stent parameters as assessed by optical coherence tomography. These findings suggest that intravascular lithotripsy can be applied to patients with both concentric and eccentric calcium morphologies to optimise stent expansion.
Acknowledgements
This paper was guest edited by Franz-Josef Neumann, MD, PhD, FESC; Department of Cardiology and Angiology II, University Heart Center Freiburg - Bad Krozingen, Bad Krozingen, Germany.
Funding
This study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Abbott.
Conflict of interest statement
N. Gonzalo has received a research grant from Abbott; and consultancy and speaker fees from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Shockwave Medical, Abiomed, and Philips. A. McInerney has received speaker fees from Shockwave Medical, Boston Scientific, and Novartis. I. Amat Santos declares acting as a proctor for Boston Scientific. A. Pérez de Prado reports receiving institutional research grants from Abbott and Shockwave Medical. A. Jurado-Roman has received speaker fees from Shockwave Medical and Abbott. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The Guest Editor reports lecture fees paid to his institution from Amgen, Bayer HealthCare, Biotronik, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Daiichi Sankyo, Edwards Lifesciences, Ferrer, Pfizer, and Novartis; consultancy fees paid to his institution from Boehringer Ingelheim; and grant support from Bayer HealthCare, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Edwards Lifesciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, and Pfizer.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

