Description
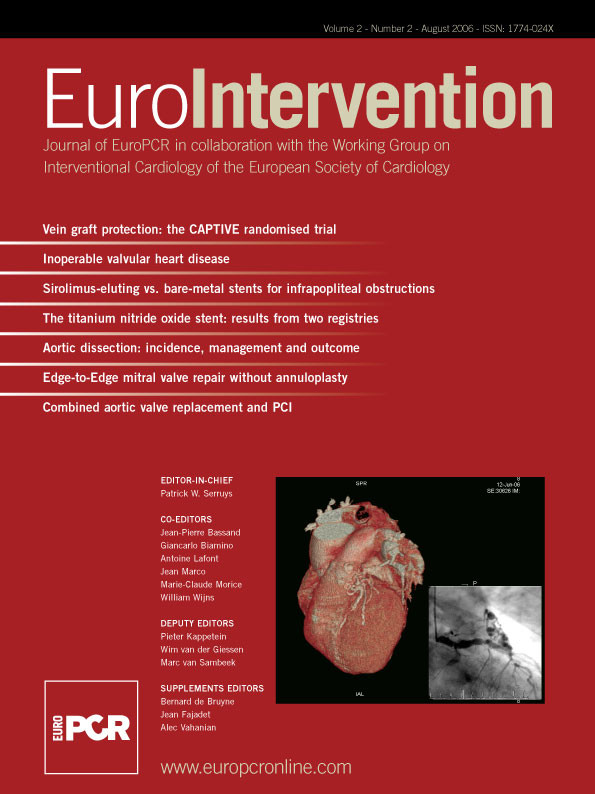
The Tryton Side-Branch Stent™ is a slotted tube balloon deployable stent with a modular design comprise of three zones: Distal (Side-Branch) Zone, Central (Transition) Zone and Proximal (Main Vessel) Zone (Figure 1).
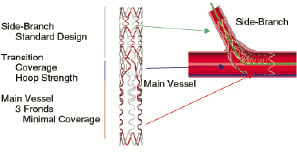
Figure 1. Schematic representing the Tryton Side-Branch Stent showing three zones: Distal (Side-Branch) Zone, Central (Transition) Zone and Proximal (Main Vessel) Zone. When positioned correctly within the vasculture the Side-Branch Zone resides in the side-branch, Transition Zone at the side-branch origin and the Main Vessel Zone in the main vessel proximal to the side-branch origin.
Tryton performs like a standard high-performance workhorse stent, i.e., balloon expandable, tracking over a single wire and axially oriented without the need for rotational orientation. The Tryton is simply tracked over a guidewire placed in the side-branch, such that the transition zone is at the side-branch origin. To insure precise delivery, the Tryton Side-Branch Stent is mounted on a balloon with four shaft markers, 2 standard proximal/distal stent markers, and 2 additional markers delineating the Transition Zone. The Tryton Stent is deployed after which the guidewire initially placed in the side-branch is repositioned into the distal main vessel. The Tryton stent is compatible with any standard workhorse stent (bare metal or DES), which is tracked into the Main Vessel Zone of the Tryton Stent and between specially designed fronds exiting into the distal main vessel stent (Figure 2).
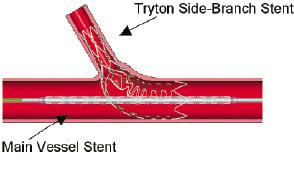
Figure 2. Schematic representing the spacial relationship between the Tryton Side-Branch Stent (deployed) with an undeployed main vessel stent. The distal end of the main vessel stent has been tracked through the proximal Main Vessel Zone of the Tryton Stent, between the specially designed fronds and into the distal main vessel.
The main vessel stent is deployed after which a kissing balloon inflation is performed. Employing this strategy provides a means to definitively treat bifurcation lesions with similar coverage and hoop strength currently available with state of the art stents used in straight lesions (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Photograph of a Tryton Side-Branch Stent deployed in a plexiglass model in combination with a Cypher Stent (Cordis/ Johnson&Johnson, Miami, FL) using the protocol outlined within main text.
History
Tryton Medical, Inc. is a privately held company with offices in Newton, Massachusetts, USA founded to develop devices to treat bifurcation lesions within the coronary, cerebral and peripheral circulations.