A 31 year old man was referred to our hospital for evaluation of recurrent angina pectoris following recent inferior-posterior myocardial infarction. His previous medical history included a surgically corrected tetralogy of Fallot at four years of age. During coronary angiography of the left anterior descending artery, a dissection of the entire vessel developed (Figure 1).
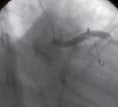
Figure 1 and Movie 1. Acute dissection of the LAD during diagnostic catheterisation.
The dissection could not be crossed with a guidewire and the patient died.
Post mortem examination was performed. Histologically, the LAD dissection channel was filled with fresh haematoma indicating recent onset (Figure 2).
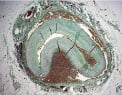
Figure 2. Cross section of the LAD showing a dissection channel in the outer part of the arterial media, filled with haematoma (Mallory’s stain).
The media showed abnormal presence of segmental ridges of medial tissue containing haphazardly arranged smooth muscle layers intermingled with elastin and collagenous tissue (Figure 3).
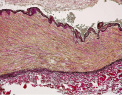
Figure 3. Detail of the coronary artery wall showing highly irregular medial ridges of fibromuscular tissue characteristic for the medial type of FMD. (Elastica van Gieson stain).
There were no signs of of inflammation (Figures 2 and 3) or previous dissections. These findings were diagnostic for the media type of fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD).
FMD is a segmental non-atherosclerotic non-inflammatory angiopathy of unknown aetiology. Renal and cervicocranial arteries are most commonly involved. Coronary FMD is very rare1. The disease is histologically classified according to the principal layer of arterial involvement (intimal-, medial- and peri-adventitial FMD). Medial FMD as found in our patient is by far (approximately 90% of cases) the commonest type.
Reference

