A 53-year-old man with hypertension and hyperlipidaemia was referred to our hospital for a third attempt to recanalise an occlusive in-stent restenosis (ISR) in the circumflex artery (LCX). In 2003, the patient had inferolateral myocardial infarction with a triple-vessel disease. Coronary bypass grafting was performed. In March 2006, stress scintigraphy for screening showed lateral ischaemia. Coronary angiography revealed an occlusion of the right internal mammary artery to a posterolateral branch. In another centre, coronary intervention was performed for subtotal occlusion in the LCX (Figure 1A). During the procedure a guidewire entered a false lumen (Figure 1B) and finally two bare metal stents were implanted with distal TIMI 2 flow (Figure 1C). Four months later, an occlusive restenosis was found. Two previous attempts failed to reopen the vessel.
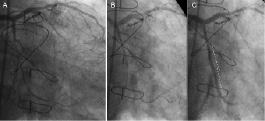
Figure 1. Initial coronary intervention for a subtotal occlusion in the LCX.
Control angiography showed occlusive ISR (Figure 2A). After crossing a guidewire and predilatation (Figure 2B), IVUS demonstrated that the distal stent was completely positioned in the false lumen and the guidewire re-entered the true lumen 18 mm distal to the stent distal edge. (Figure 2a-e).
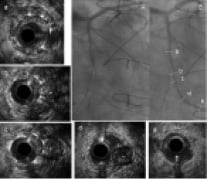
Figure 2. Control angiography with IVUS revealing occlusive in-stent restenosis.
The true lumen (*) was observed out of stent struts. Angiography with IVUS transducer positioned at the re-entry point (Figure 3A, arrow) was performed for a guide to optimal stenting and three sirolimus eluting stents (SES) were implanted with excellent angiographic result (Figure 3B). Post-intervention IVUS confirmed SES covered entire false lumen and connected the proximal true lumen with the distal one. The vessel was open at four months follow-up (Figure 3C).
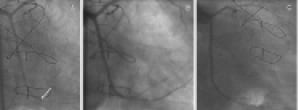
Figure 3. Coronary angiography with implantation of 3 sirolimus-eluting stents.

