Objective
to investigate the safety and efficacy of TriGuard HDH (TG) cerebral embolic protection device compared to controls in patients undergoing TAVI
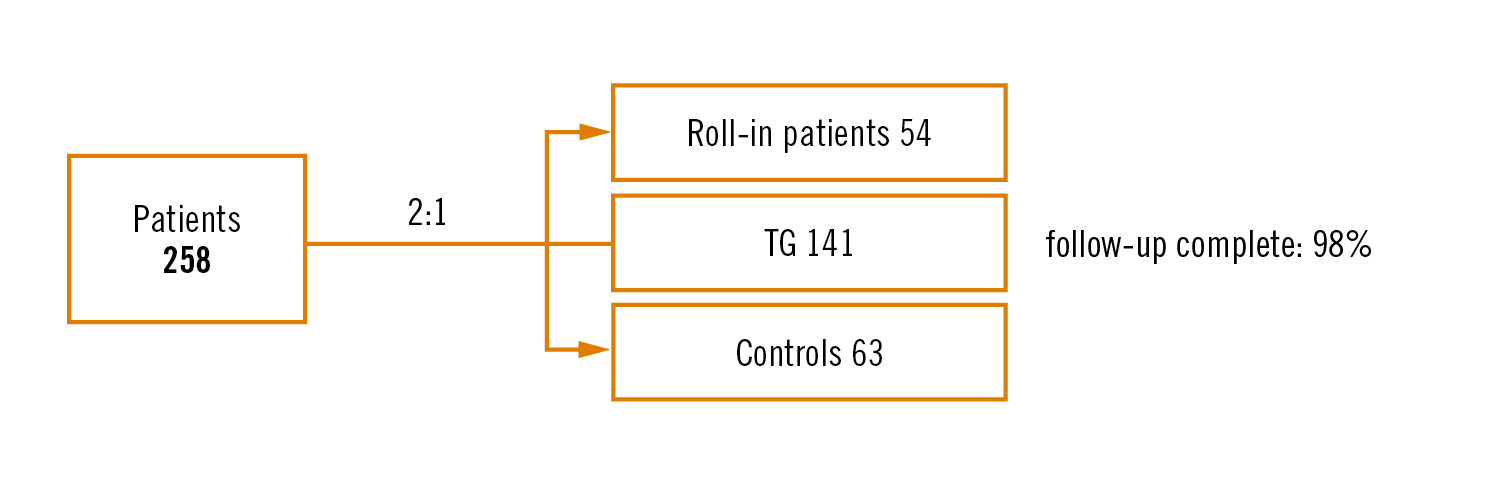
Study
prospective, multicentre, single-blind 2:1 (TG vs no TG) randomised trial
Population
patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis referred for TAVI
Endpoints
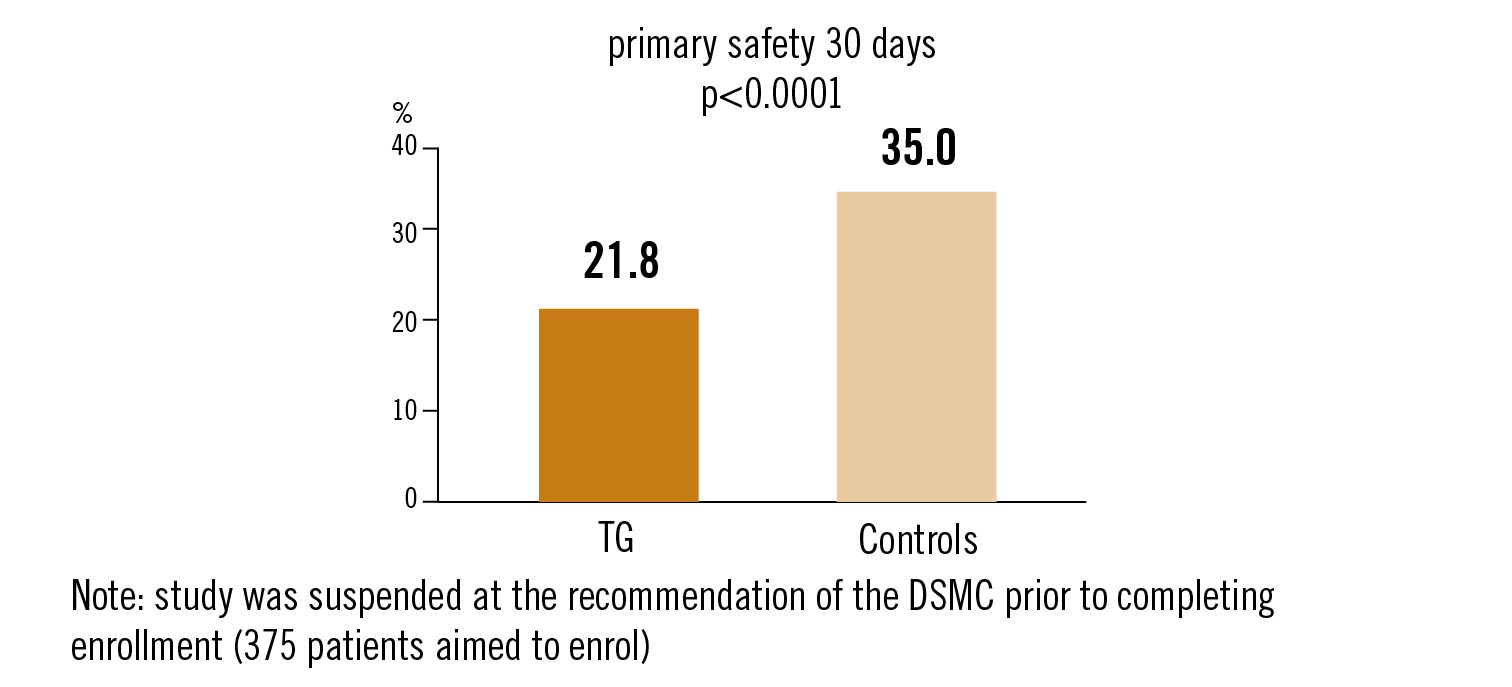
safety endpoint: composite of all-cause death, stroke, severe bleeding, stage 2-3 acute kidney injury, coronary obstruction, major vascular complications, valve related dysfunction at 30 days.
efficacy endpoint: all-cause death or any stroke at 30 days, NIHSS or MoCA worsening at 30 days and MRI-lesions.
Conclusion
TriGuard cerebral protection is safe but did not meet the primary effectiveness endpoint compared to controls
Lansky et al. European Heart Journal. 2021;42:2670-79



