Objective
to report the 8-year clinical outcomes of surgical as compared to transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Study
investigator-initiated multicentre randomised trial
Population
patients aged â¥70 years with severe aortic valve stenosis at lower surgical risk
Endpoints
valve durability was divided into bioprosthetic valve dysfunction (BVD) and bioprosthetic valve failure (BVF) (EACTS criteria).
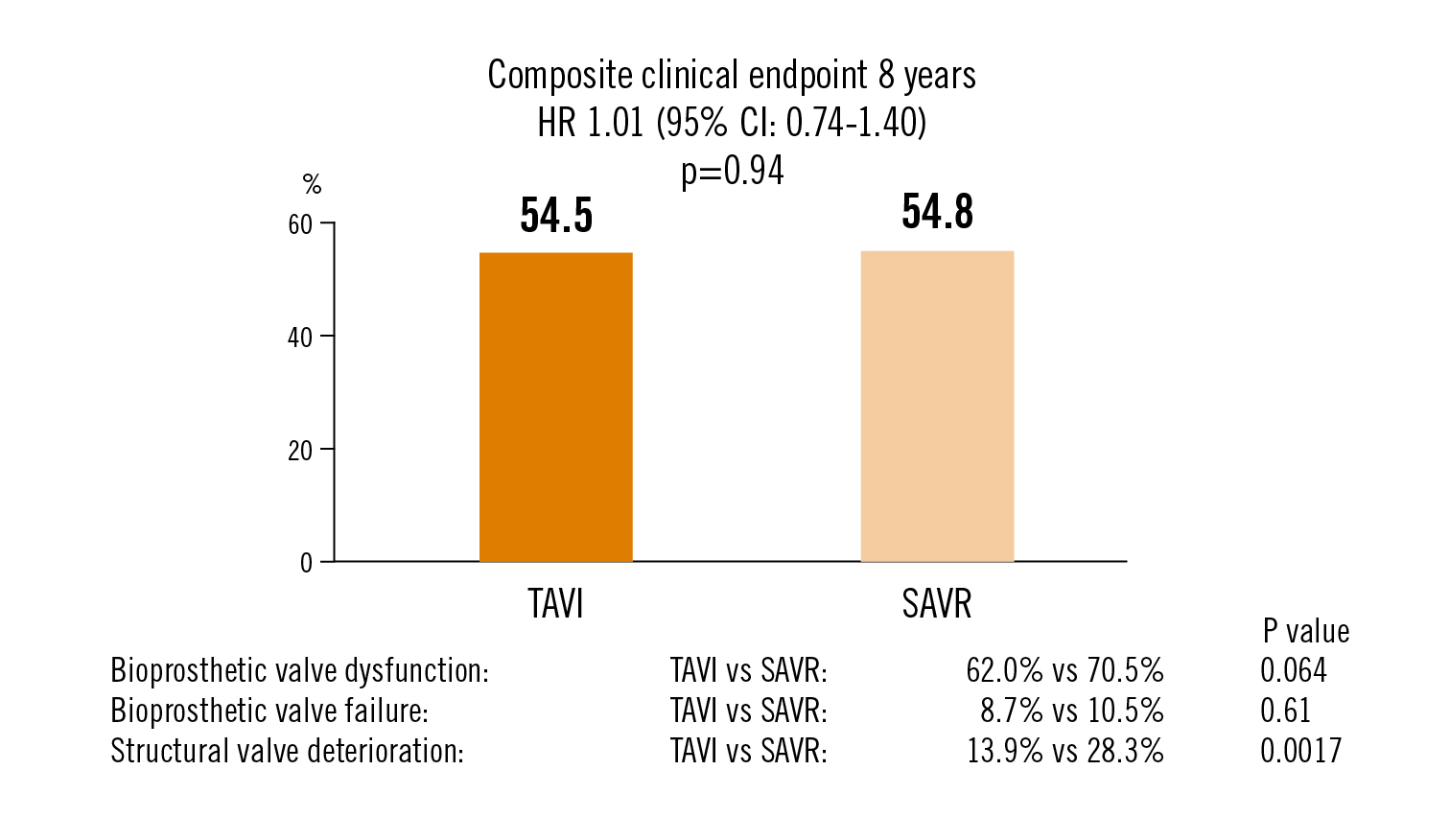
Composite clinical endpoint: all-cause death, stroke, MI
Conclusion
in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk there were no significant differences in risk of MACE and bioprosthetic valve dysfunction or failure during 8-year follow-up in patients with TAVI or SAVR. Structural valve deterioration was lower after TAVI
Hosguard et al. European Heart Journal. 2021;42:2912-19



