Objective
to assess the safety and efficacy of catheter-based renal denervation for treatment of moderate uncontrolled hypertension despite treatment
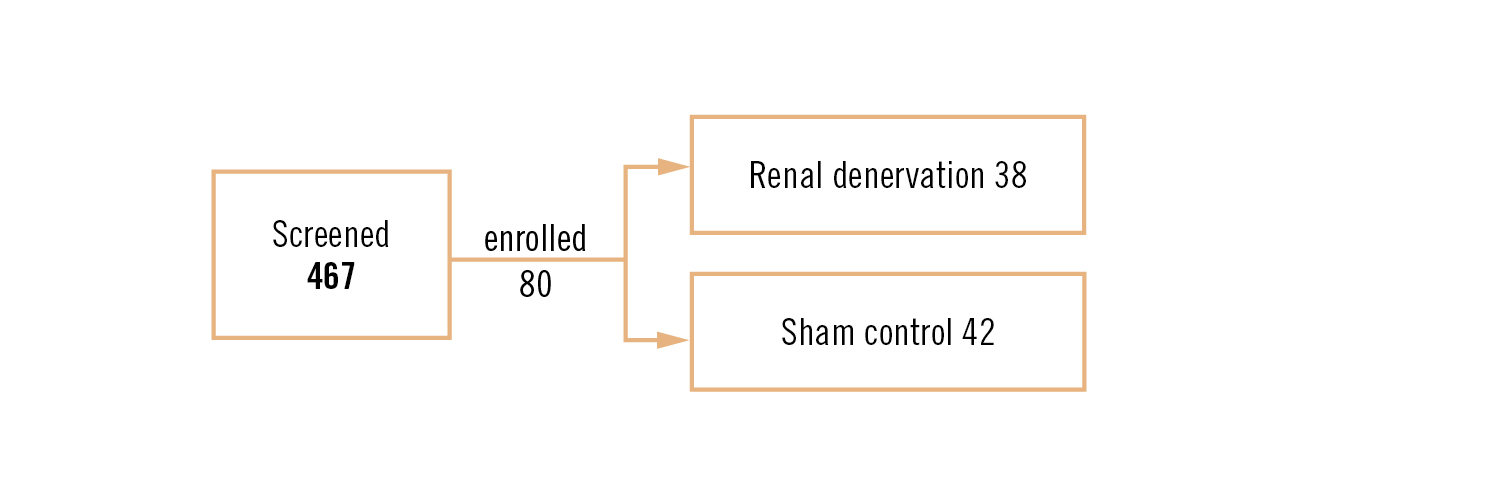
Study
multicentre, randomised sham-controlled, blinded trial
Population
patients with office systolic blood pressure between 150 and 180 mmHg, or office diastolic pressure 90 mmHg or higher and mean 24h ambulatory systolic blood pressure between 140 and 170 mmHg. Patients were on standard treatment with 1, 2 or 3 antihypertensive drugs
Endpoints
blood pressure change from baseline based on ambulatory blood pressure measurements at 6 months

Conclusion
renal denervation in the main renal arteries and branches reduced the blood pressure compared to sham controlled patients
Kandzari et al. Lancet. 2018;391:2346-55



