Objective
to determine whether PCI (plus optimal medical treatment: OMT) can improve adverse clinical outcomes as compared to optimal medical treatment alone (OMT) in patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction
Study
prospective, multicentre, randomised trial
Population
patients with LV ejection fraction ⤠35% and extensive CAD (BCIS jeopardy score of ⥠6) and demonstrable viability in at least 4 dysfunctional myocardial segments amenable to revascularisation with PCI
Endpoints
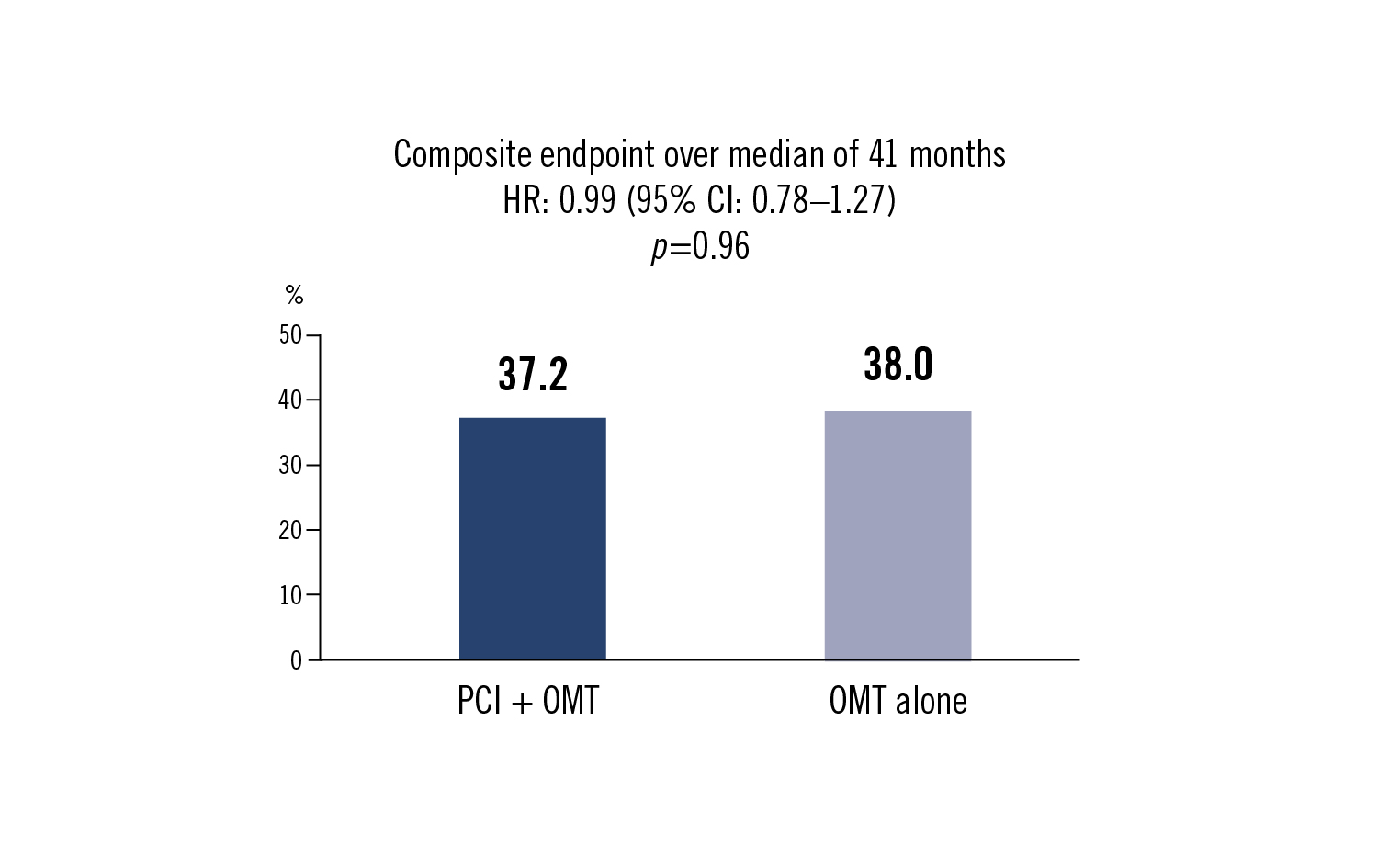
composite of any-cause death or hospitalisation for heart failure
Conclusion
in patients with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction, extensive CAD and viable myocardium PCI in addition to optimal medical treatment did not improve the incidence of death or hospitalisation for heart failure compared to optimal medical treatment alone.
Perera et al N Engl J Med. 2022;387:1351-60



