Objective
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of temporary mechanical circulatory support with a microaxial flow pump on mortality among patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) complicated by cardiogenic shockas compared to standard therapy alone
Study
Prospective, open-label multicentre randomised trial
Population
Patients with infarct related cardiogenic shock
Endpoints
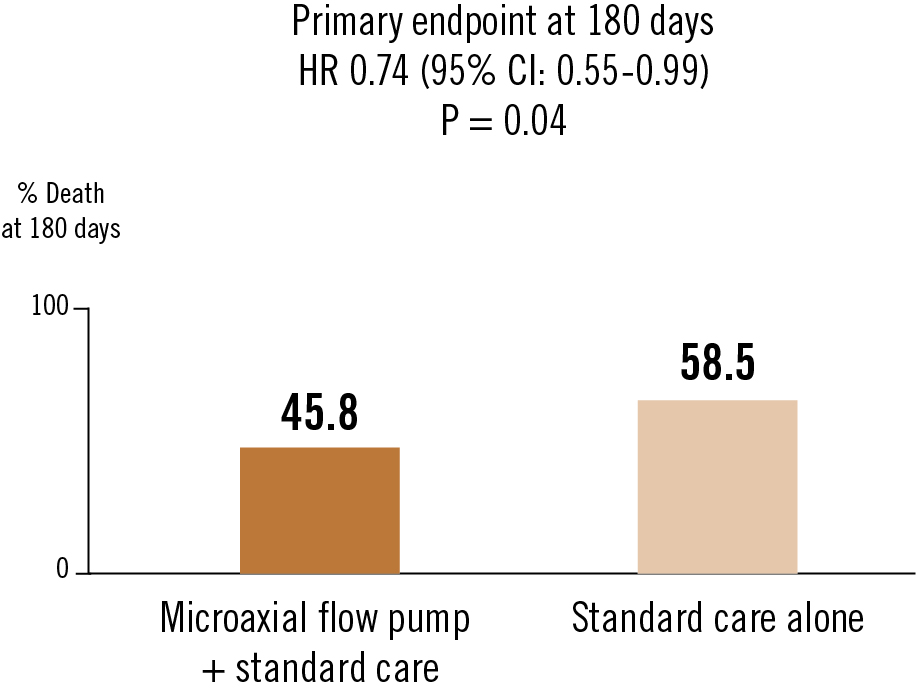
Primary endpoint: death from any cause at 180 days
Conclusion
Routine use of a microaxial flow pump in the treatment of patients with STEMI-related cardiogenic shock led to a lower risk of death from any cause at 180 days than standard care alone, though the incidence of a composite of adverse events was higher with the use of the microaxial flow pump.
Møller et al. NEJM 2024 April



