Objective
to assess the clinical adverse outcomes of direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC’s) compared to left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation
Study
investigation-initiated, prospective, multicentre non-inferiority randomised trial (margin 5%)
Population
high risk patients (CHA2DS2-VASC ≥3) with atrial fibrillation
Endpoints
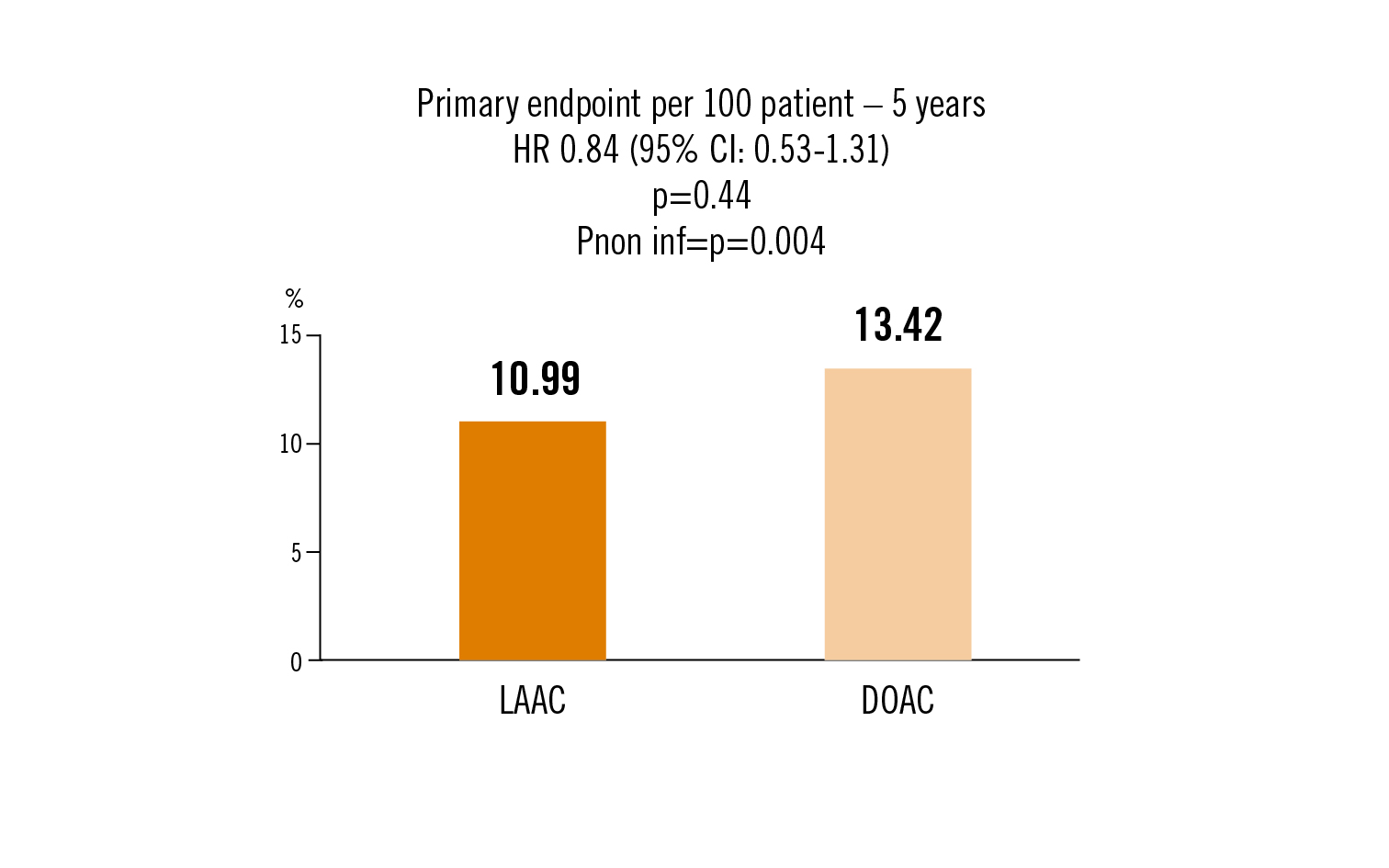
stroke, TIA, systemic embolism, cardiovascular death, major or non major clinical relevant bleeding or procedure/ device related complications
Conclusion
LAAC was non-inferior to DOAC in preventing adverse events in high- risk patients with atrial fibrillation
Osmancik et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35



