Objective
to assess the clinical outcome of FFR versus OCT to guide the management of intermediate coronary stenosis
Study
single centre prospective randomised trial
Population
patients with stable ischemic heart disease and visually assessed coronary lesion ranging between 30% and 80% PCI if FFR â¤0.80 or OCT if area stenosis â¥75%
Endpoints
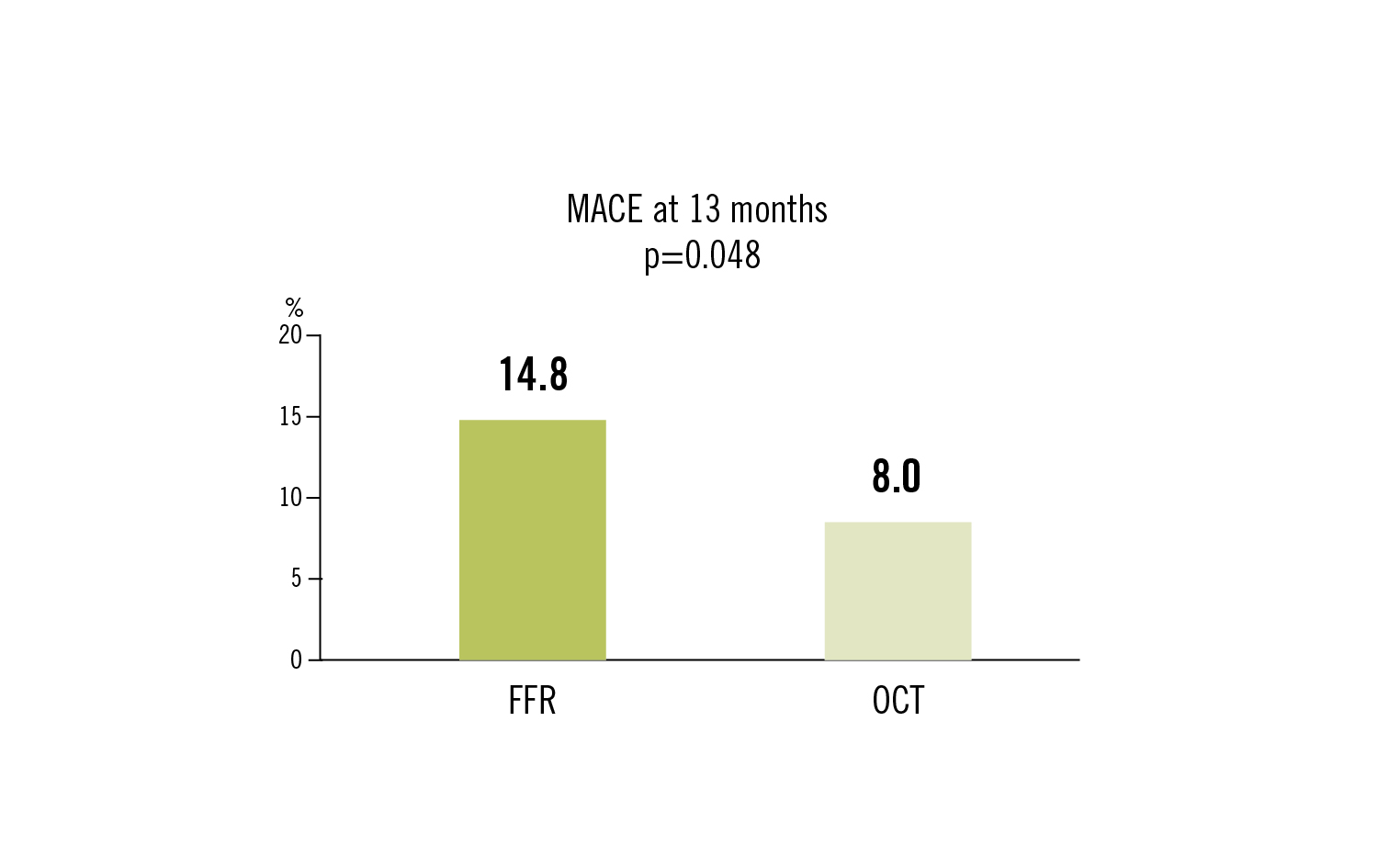
combination of all-cause death, non fatal MI, target vessel revascularisation and significant angina at 13 months
Conclusion
OCT guidance is associated with lower occurrence of MACE or significant angina during 13 month follow up
Burzotta et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;13:49-58



