Objective
to investigate whether immediate implementation of extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) as compared to conservative therapy for cardiogenic shock in more effective
Study
investigator-initiated, multicentre, randomised trial
Population
patients with rapidly deteriorating or severe cardiogenic shock
Endpoints
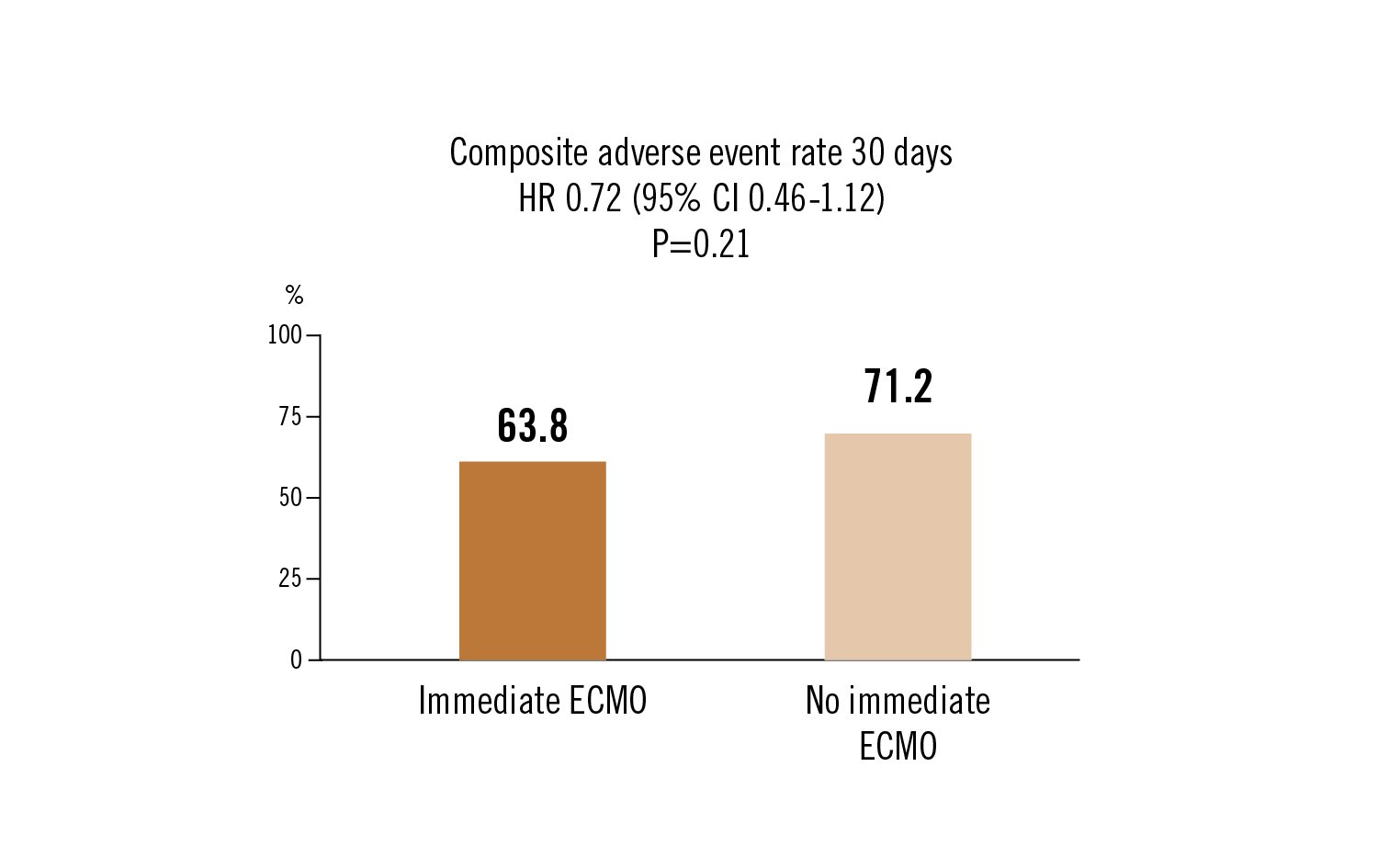
composite of any-death, resuscitated cardiac arrest or implementation other mechanical circulatory support at 30 days
Conclusion
adverse clinical outcomes did not improve with immediate ECMO compared to no immediate ECMO for patients with rapidly deteriorating or severe cardiogenic shock
Ostadal et al. Circulation 2023:147: 454-464



